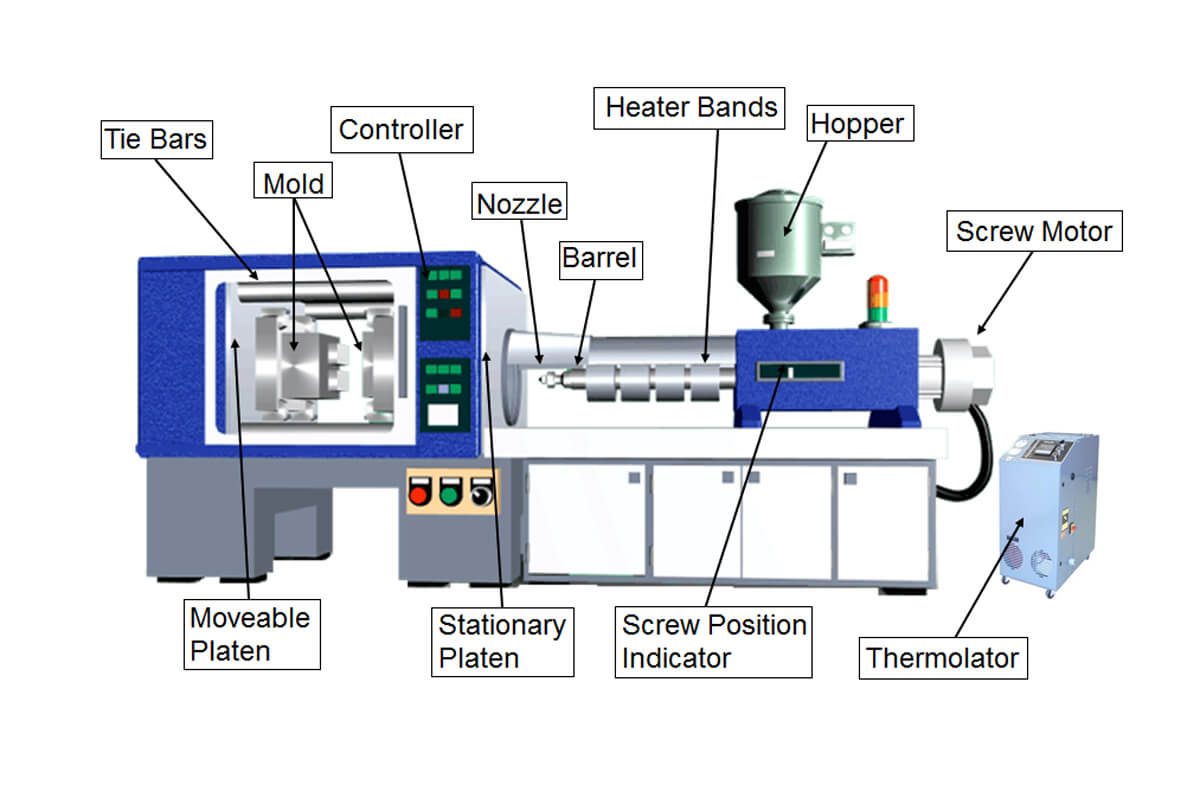
Injection Molding Machine Introduction Technology: Injection molding is an engineering technology that involves transforming plastic into useful and original products. The important process conditions for injection molding are the temperature, pressure and corresponding individual time of action that affect plasticizing flow and cooling.
First, temperature control
1. Barrel temperature: The temperature to be controlled during the injection molding process includes the barrel temperature, nozzle temperature and mold temperature. The first two temperatures primarily affect the plasticization and flow of the plastic, while the latter temperature primarily affects the flow and cooling of the plastic. Each plastic has a different flow temperature. The same plastic has different flow and decomposition temperatures due to different sources or grades. This is due to the difference in average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution. Plastics are injected in different types. The plasticizing process in the machine is also different, so the temperature of the selected cylinder is also different.
2. Nozzle temperature: The nozzle temperature is usually slightly lower than the maximum temperature of the barrel. This is to prevent the "flowing phenomenon" of the melt in the straight-through nozzle. The nozzle temperature should not be too low, otherwise it will cause early condensation of the melt to block the nozzle, or affect the performance of the product due to the injection of the early aggregate into the cavity.
3. Mold temperature: The mold temperature has a great influence on the intrinsic properties and apparent quality of the product. The temperature of the mold depends on the presence or absence of crystallinity of the plastic, the size and structure of the product, performance requirements, and other process conditions (melt temperature, injection speed and injection pressure, molding cycle, etc.).
Second, pressure control
The pressure during the injection molding process includes plasticizing pressure and injection pressure, and directly affects the plasticization of plastics and the quality of products.
1. Plasticizing pressure: (back pressure) When using a screw type injection machine, the pressure that the top melt of the screw receives when the screw rotates backward is called plasticizing pressure, also known as back pressure. This pressure can be adjusted by a relief valve in the hydraulic system.
In the injection, the plasticizing pressure is constant with the rotation speed of the screw. When the plasticizing pressure is increased, the temperature of the melt is increased, but the plasticizing speed is reduced. In addition, increasing the plasticizing pressure often makes the temperature of the melt uniform, the mixing of the colorant uniform, and the discharge of the gas in the melt. In general operation, the determination of plasticizing pressure should be as low as possible to ensure the quality of the product. The specific value varies with the type of plastic used, but usually rarely exceeds 20 kg/cm 2 .
2 Injection pressure: In the current production, the injection pressure of almost all injection machines is based on the pressure exerted by the plunger or the top of the screw on the plastic (converted from the oil pressure). The injection pressure plays a role in injection molding by overcoming the flow resistance of the plastic from the barrel to the cavity, giving the melt filling rate and compacting the melt.
Third, the molding cycle
The time required to complete an injection molding process is called the molding cycle, also known as the molding cycle. It actually includes the following parts:
Molding cycle: The molding cycle directly affects labor productivity and equipment utilization. Therefore, in the production process, the relevant time in the molding cycle should be shortened as much as possible under the premise of ensuring the quality. Injection time and cooling time are of the utmost importance throughout the molding cycle and they have a decisive influence on the quality of the product. The filling time in the injection time is directly inversely proportional to the filling rate, and the filling time in production is generally about 3-5 seconds.
The holding time in the injection time is the pressure time of the plastic in the cavity, which accounts for a large proportion in the whole injection time, generally about 20-120 seconds (the extra-thick parts can be as high as 5-10 minutes). Before the melting of the melt at the gate, the amount of dwell time has an effect on the dimensional accuracy of the product. If it is later, it has no effect. The holding time also has the best value, which is known to depend on the material temperature, the mold temperature and the size of the main runners and gates. If the size and process conditions of the main runners and gates are normal, it is usually the value of the pressure at which the range of fluctuation of the shrinkage of the product is the smallest.
The cooling time is mainly determined by the thickness of the product, the thermal properties and crystallization properties of the plastic, and the temperature of the mold.
The end point of the cooling time should be based on the principle of ensuring that the product does not cause changes during demolding. The cooling time is generally between 30 and 120 seconds. The cooling time is not necessary, which not only reduces the production efficiency, but also complicates the complicated parts. It is difficult to release the mold, and even the mold release stress is generated when the mold is released. Other times in the molding cycle are related to whether the production process is continuous and automated, as well as the degree of continuity and automation.
The general injection molding machine can be adjusted according to the following procedures:
Adjust the barrel temperature to the middle of the range and adjust the mold temperature based on the temperature range provided by the material supplier's data.
Estimate the amount of glue required to adjust the injection molding machine to two-thirds of the estimated maximum shot size. Adjust the backstrip (pumping) stroke. Estimate and adjust the secondary injection time and adjust the secondary injection pressure to zero.
Initially adjust the first-stage injection pressure to half (50%) of the limit of the injection molding machine; adjust the injection speed to the highest. Estimate and adjust the cooling time required. Adjust the back pressure to 3.5 bar. The degraded resin in the cartridge is removed. Use semi-automatic injection molding mode; start the injection molding process and observe the action of the screw.
The injection speed and pressure can be appropriately adjusted as needed, and if the filling time is shortened, the injection pressure can be increased. As mentioned earlier, the final pressure of the filling can be adjusted to 100% of the primary injection pressure due to a process before the full filling. The pressure must eventually be adjusted high enough so that the maximum speed that can be achieved is not limited by the set pressure. If there is a flash, you can reduce the speed.
After each observation period, the amount of glue and the switching point are adjusted. The setting procedure is such that it is possible to obtain a 95-98% filling of the shot weight in the first stage of injection molding.
When the injection volume, switching point, injection speed and pressure of the first-stage injection molding are properly adjusted, the second-stage pressure maintaining pressure adjustment procedure can be performed.
Adjust the holding pressure as needed, but do not overfill the cavity.
The screw speed is adjusted to ensure that the melt is completed just before the cycle is completed and the injection cycle is not limited.
Reduce cycle time to increase productivity
For most injection molders, the injection cycle can directly affect two main purposes:
1. Get more parts from the machine every day;
2. The parts meet the requirements of the guests.
First, temperature control
1. Barrel temperature: The temperature to be controlled during the injection molding process includes the barrel temperature, nozzle temperature and mold temperature. The first two temperatures primarily affect the plasticization and flow of the plastic, while the latter temperature primarily affects the flow and cooling of the plastic. Each plastic has a different flow temperature. The same plastic has different flow and decomposition temperatures due to different sources or grades. This is due to the difference in average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution. Plastics are injected in different types. The plasticizing process in the machine is also different, so the temperature of the selected cylinder is also different.
2. Nozzle temperature: The nozzle temperature is usually slightly lower than the maximum temperature of the barrel. This is to prevent the "flowing phenomenon" of the melt in the straight-through nozzle. The nozzle temperature should not be too low, otherwise it will cause early condensation of the melt to block the nozzle, or affect the performance of the product due to the injection of the early aggregate into the cavity.
3. Mold temperature: The mold temperature has a great influence on the intrinsic properties and apparent quality of the product. The temperature of the mold depends on the presence or absence of crystallinity of the plastic, the size and structure of the product, performance requirements, and other process conditions (melt temperature, injection speed and injection pressure, molding cycle, etc.).
Second, pressure control
The pressure during the injection molding process includes plasticizing pressure and injection pressure, and directly affects the plasticization of plastics and the quality of products.
1. Plasticizing pressure: (back pressure) When using a screw type injection machine, the pressure that the top melt of the screw receives when the screw rotates backward is called plasticizing pressure, also known as back pressure. This pressure can be adjusted by a relief valve in the hydraulic system.
In the injection, the plasticizing pressure is constant with the rotation speed of the screw. When the plasticizing pressure is increased, the temperature of the melt is increased, but the plasticizing speed is reduced. In addition, increasing the plasticizing pressure often makes the temperature of the melt uniform, the mixing of the colorant uniform, and the discharge of the gas in the melt. In general operation, the determination of plasticizing pressure should be as low as possible to ensure the quality of the product. The specific value varies with the type of plastic used, but usually rarely exceeds 20 kg/cm 2 .
2 Injection pressure: In the current production, the injection pressure of almost all injection machines is based on the pressure exerted by the plunger or the top of the screw on the plastic (converted from the oil pressure). The injection pressure plays a role in injection molding by overcoming the flow resistance of the plastic from the barrel to the cavity, giving the melt filling rate and compacting the melt.
Third, the molding cycle
The time required to complete an injection molding process is called the molding cycle, also known as the molding cycle. It actually includes the following parts:
Molding cycle: The molding cycle directly affects labor productivity and equipment utilization. Therefore, in the production process, the relevant time in the molding cycle should be shortened as much as possible under the premise of ensuring the quality. Injection time and cooling time are of the utmost importance throughout the molding cycle and they have a decisive influence on the quality of the product. The filling time in the injection time is directly inversely proportional to the filling rate, and the filling time in production is generally about 3-5 seconds.
The holding time in the injection time is the pressure time of the plastic in the cavity, which accounts for a large proportion in the whole injection time, generally about 20-120 seconds (the extra-thick parts can be as high as 5-10 minutes). Before the melting of the melt at the gate, the amount of dwell time has an effect on the dimensional accuracy of the product. If it is later, it has no effect. The holding time also has the best value, which is known to depend on the material temperature, the mold temperature and the size of the main runners and gates. If the size and process conditions of the main runners and gates are normal, it is usually the value of the pressure at which the range of fluctuation of the shrinkage of the product is the smallest.
The cooling time is mainly determined by the thickness of the product, the thermal properties and crystallization properties of the plastic, and the temperature of the mold.
The end point of the cooling time should be based on the principle of ensuring that the product does not cause changes during demolding. The cooling time is generally between 30 and 120 seconds. The cooling time is not necessary, which not only reduces the production efficiency, but also complicates the complicated parts. It is difficult to release the mold, and even the mold release stress is generated when the mold is released. Other times in the molding cycle are related to whether the production process is continuous and automated, as well as the degree of continuity and automation.
The general injection molding machine can be adjusted according to the following procedures:
Adjust the barrel temperature to the middle of the range and adjust the mold temperature based on the temperature range provided by the material supplier's data.
Estimate the amount of glue required to adjust the injection molding machine to two-thirds of the estimated maximum shot size. Adjust the backstrip (pumping) stroke. Estimate and adjust the secondary injection time and adjust the secondary injection pressure to zero.
Initially adjust the first-stage injection pressure to half (50%) of the limit of the injection molding machine; adjust the injection speed to the highest. Estimate and adjust the cooling time required. Adjust the back pressure to 3.5 bar. The degraded resin in the cartridge is removed. Use semi-automatic injection molding mode; start the injection molding process and observe the action of the screw.
The injection speed and pressure can be appropriately adjusted as needed, and if the filling time is shortened, the injection pressure can be increased. As mentioned earlier, the final pressure of the filling can be adjusted to 100% of the primary injection pressure due to a process before the full filling. The pressure must eventually be adjusted high enough so that the maximum speed that can be achieved is not limited by the set pressure. If there is a flash, you can reduce the speed.
After each observation period, the amount of glue and the switching point are adjusted. The setting procedure is such that it is possible to obtain a 95-98% filling of the shot weight in the first stage of injection molding.
When the injection volume, switching point, injection speed and pressure of the first-stage injection molding are properly adjusted, the second-stage pressure maintaining pressure adjustment procedure can be performed.
Adjust the holding pressure as needed, but do not overfill the cavity.
The screw speed is adjusted to ensure that the melt is completed just before the cycle is completed and the injection cycle is not limited.
Reduce cycle time to increase productivity
For most injection molders, the injection cycle can directly affect two main purposes:
1. Get more parts from the machine every day;
2. The parts meet the requirements of the guests.